Last Updated:November 28, 2025, 14:56 IST
A black hole 400 million times the Sun’s mass has erupted, sending a record-breaking gamma-ray flare towards Earth. The event reveals the violent power of the universe

This discovery is pivotal for understanding jet formation and the physics of supermassive black holes. (AI Generated)
A dormant ‘monster’ in space has erupted. Scientists have directly observed a black hole unleashing a ferocious burst of energy. Most alarming is that the cosmic cannon of this black hole, a blazar, is aimed almost directly at Earth.
Astronomers recorded the most powerful gamma-ray flare ever detected, with signals travelling millions of light-years. This extraordinary event demonstrates the violent and unpredictable nature of our universe. The blazar responsible is named TXS 2013+370, which suddenly intensified in brightness and unleashed a massive storm of energy.
A Cosmic Gun Pointed At Earth
Blazars are among the most mysterious and fearsome objects in the cosmos. They are supermassive black holes at the centre of active galaxies, consuming surrounding matter and releasing tremendous energy. The material is ejected in jets that travel at the speed of light.
The defining feature of a blazar is that one of these jets points almost directly at Earth, akin to a loaded gun aimed at us. TXS 2013+370 is one such blazar and is the largest known source of gamma-ray bursts outside our galaxy.
A Black Hole 400 Million Times Heavier Than The Sun
The scale of this black hole is staggering. Scientists estimate it to be 400 million times the mass of our Sun, a truly unfathomable magnitude.
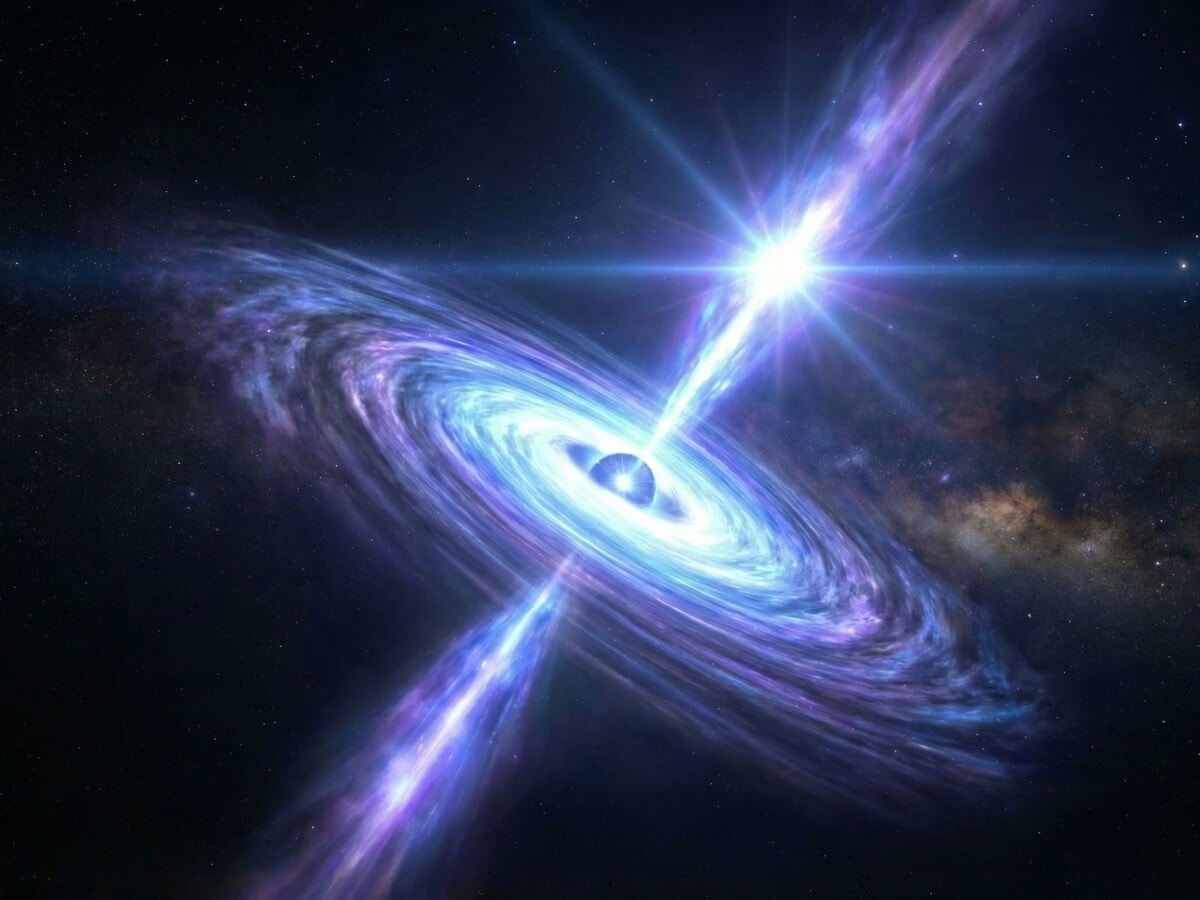

Located near the plane of the Milky Way, TXS 2013+370 began exhibiting unusual activity on December 6, 2020, with its gamma-ray emissions intensifying, a precursor to the subsequent massive flare. The black hole began intermittent flaring, prompting astronomers to focus their telescopes on the object immediately.
Record-Breaking Gamma-Ray Flare
A team led by Giorgos Michaelides at Aristotle University of Greece utilised the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), a powerful network of radio telescopes, to capture the blazar’s extraordinary flare on February 11, 2021. Observations at 22, 43, and 86 GHz provided the most detailed images of a blazar to date.
This research, posted on a pre-print server on November 19, reveals the intricate details of this cosmic explosion.
Black Hole vs Blazar: What’s The Difference?
While all blazars are black holes, not all black holes are blazars. A blazar is specifically an active black hole whose relativistic jet is aligned towards Earth, producing intense radiation detectable across multiple wavelengths.
The study uncovered a surprising discovery: the jet from TXS 2013+370 is curved toward the southwest, rather than perfectly straight. A new component, ‘N2’, has appeared within the jet, located close to the blazar’s main centre. Multi-wavelength activity is concentrated here, indicating significant energetic processes inside the black hole.
Higher frequencies allowed scientists to resolve the jet’s structure with unprecedented clarity.
Gamma-Rays Precede Radio Signals
Scientists observed a strong correlation between gamma-ray and radio emissions, with gamma-ray activity leading radio waves by approximately 102 days. This time delay suggests that high-energy gamma rays are emitted first, potentially serving as an early warning for upcoming radio bursts.
The team believes this emission originates from a dusty torus, a vast cloud of dust encircling the black hole. When the jet collides with this photon-rich dust, immense energy is released.
Comparisons with a similar burst in 2009 revealed that gamma-ray activity occurs in roughly the same sub-parsec region, indicating dynamic, ever-changing conditions around the black hole.
Implications For Black Hole Physics
This discovery is pivotal for understanding jet formation and the physics of supermassive black holes. TXS 2013+370 is not a passive object; it actively exerts power, shaping its surrounding universe.
The insights gained from these observations will help astronomers decode the workings of black holes and predict future energetic events.
First Published:
November 28, 2025, 14:56 IST
News world Black Hole Blazar 400 Million Times Heavier Than The Sun Is Firing Deadly Rays At Earth
Disclaimer: Comments reflect users’ views, not News18’s. Please keep discussions respectful and constructive. Abusive, defamatory, or illegal comments will be removed. News18 may disable any comment at its discretion. By posting, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Read More

 2 hours ago
2 hours ago